Appearance
Transfer ERC20s Between Layer 1 and Layer 2
Introduction
This tutorial will guide you through the process of using the Reddio API to deposit, transfer, and withdraw ERC20 between the Ethereum layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains using typescript.
You can get the Transfer ERC20s Between Layer 1 and Layer 2 project from github. After you cloned the project in your device, you can use following prompts to install all the dependencies.
bash
yarn installAfter install all the dependencies, use following prompts to start the project:
bash
yarn startNow we will go over important components of our project.
Testing parameters
During your application implementation. There shall be a form asks for ERC20 contract address. For testing purpose only, we will use the RDD20 as an example. RDD20 is the ERC20s we use in Reddio’s demo. The RDD20’s contract address on Sepolia testnet is:
bash
0x57F3560B6793DcC2cb274c39E8b8EBa1dd18A086Connect to wallet
If you want to deposit, transfer, and withdraw tokens between the Ethereum layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains, you need to connect to your wallet first. We will use Metamask as an example to show you how to connect to the wallet and create Stark keypairs based on it. There’s one thing to note that one Metamask wallet address will generate the same Stark keypair.
tsx
async function connectToWallet() {
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') {
//First, get the web3 provider if window is not undefined
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
//Second, we need to ask the wallet to switch to specific ETH network
//We will use Sepolia testnet to give example.Its hexValue is 11155111.
await provider.send("wallet_switchEthereumChain", [
{ chainId: ethers.utils.hexValue(11155111) },
]);
//Third, getting the account addresses from provider
await provider.send('eth_requestAccounts', []);
const signer = provider.getSigner();
const ethAddress = await signer.getAddress();
//Finally, we can create a new reddio instance (Sepolia testnet)
//And assign global variable to it
const reddio = new Reddio({
provider,
env: 'test',
});
setReddio(reddio);
const generateKey = async () => {
try {
//Generate stark private key and public key
//Store them into array
const { privateKey, publicKey } = await reddio.keypair.generateFromEthSignature();
//We will set ethAddress/starkKey/privateKey on our array
setEventValue({ ...eventValue, ethAddress, starkKey: publicKey, privateKey })
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
generateKey();
}
}After you start the project. You will see a “Connect wallet” button in the main page, after clicking on the button. MetaMask will show up and ask you to login.
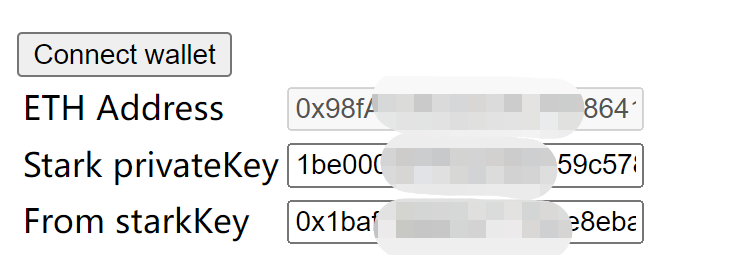
After login into your wallet, your address will be shown on the “ETH Address”. And your stark key and stark private key will be shown on the forms. If you see your wallet’s address, that means your wallet is successfully connected to the application.
Deposit: from layer 1 to layer 2
If you want to trade on layer 2, you need to have assets on layer 2. So you need to deposit your assets from layer 1 to layer 2 at first. We will use RDD20 (ERC20 that published by Reddio for testing purpose) to give example. You can get your own RDD20 by going to the demo page and click on the “Get test assets” button to get some RDD20.
Now, we will show you how to implement the deposit function in your application.
tsx
async function depositERC20() {
//Authorize the ERC20 contract address to approve the transaction
if (reddio !== null) {
const { starkKey, tokenAmount, contractAddress } = eventValue
const transaction = await reddio.erc20.approve({
//Amounts that you want to approve
amount: tokenAmount,
//ERC20's contract address
tokenAddress: contractAddress,
})
//Waiting for approval
await transaction?.wait()
//Deposit ERC20
await reddio.apis.depositERC20({
//Your starkKey (public key on layer 2)
starkKey,
//Amounts you want to deposit
quantizedAmount: tokenAmount,
//ERC20's contract address
tokenAddress: contractAddress,
});
}
}After you write down the proper information on the forms and click on the deposit button, your MetaMask will ask you to confirm all the transactions. After that, you can check your balance.
Transfer: from layer 2 to layer 2
After deposit, you have your own RDD20 tokens on layer 2. Now you want to send the RDD20 tokens to others on layer 2.
Now, we will show you how to implement the transfer function in your application.
tsx
async function transferERC20() {
if (reddio !== null) {
const { starkKey, privateKey, tokenAmount, contractAddress, receiver } = eventValue
//transfer the amount to another starkKey
const { data: res } = await reddio.apis.transfer({
starkKey,
privateKey,
contractAddress,
amount: tokenAmount,
type: 'ERC20',
receiver,
});
console.log(res);
}
}After you write down the proper information on the forms and click on the transfer button. You can check a response from your console likes the picture down below:

Transfering ERC20 tokens on layer 2 is quick. You can check your balance very soon.
Withdraw: from layer 2 to layer 1
You already have a lot of ERC20 tokens on layer 2. You want these tokens back to your layer 1 wallet.
Now, we will show you how to implement the withdraw function in your application. Typically, withdraw methods are composed by two steps: withdraw from layer 2 to withdraw area and then withdraw th from layer 1.
The first step at least takes about 4 hour. You can check withdraw status here.
tsx
async function withdrawERC20FromL2() {
if (reddio !== null) {
const { starkKey, privateKey, tokenAmount, contractAddress, receiver } = eventValue
//Step 1: withdraw tokens from layer 2 (usually takes 4 hour)
const { data } = await reddio.apis.withdrawalFromL2({
starkKey,
privateKey,
amount: tokenAmount,
contractAddress,
type: "ERC20",
receiver,
});
console.log(data);
}
}The second step is to withdraw the assets from layer 1. You can refer to guide here